Our ability to identify and differentiate sounds improves with practice, but how the brain adapts to particularly difficult listening tasks is not fully understood. In this study, we explored how brain cells in the auditory cortex of mice respond when faced with sound discrimination tasks of varying difficulty. Using behavioral manipulations (changing the task from easy to hard) and advanced imaging techniques (single neuron imaging during behavior), we found that single neurons in the cortex rapidly enhance their responses in order to be able to discriminate the more difficult sounds. This rapid adaptability, occurs only after learning and shows how the brain can enhance its performance when needed.
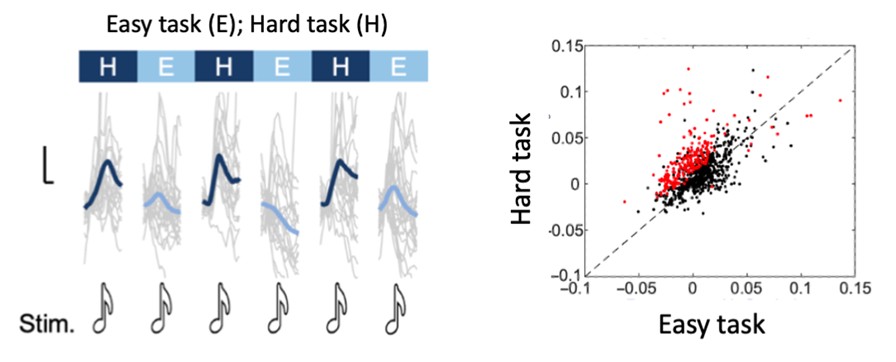
Figure Caption: Left: A response of a single neuron in the cortex to the same sound when the animal is engaged in an easy (E) and a hard task (H). Right: Responses of all neurons in the easy and hard task. The dots marked red are neurons that significantly increased their responses.
